Maps for Milvus milvus#
Alexander Dunkel, Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development, Transformative Capacities & Research Data Centre (IÖR-FDZ)
Publication:
Dunkel, A., Burghardt, D. (2024). Assessing perceived landscape change from opportunistic spatio-temporal occurrence data. Land 2024
Summary
In this section we intend to share additional notebooks on various topics in spatial visualisation, prepared by colleagues for specific projects or publications.
This sample notebook on exploration of “Milvus milvus” observations (Red Kite) on iNaturalist has been prepared and shared in a data repository specifically for replicating figures in a publication (Dunkel & Burghardt 2024(Dunkel and Burghardt 2024)). It is shared as is, as an example to document a real publication workflow. We do not provide any dependency setup. This notebook was last updated on Aug-19-2023, Carto-Lab Docker, version 0.14.0. If you want to replicate this notebook, either install the dependencies manually or use the appropriate Carto-Lab Docker container archive version which includes all dependencies.
Last updated: Aug-19-2023, Carto-Lab Docker Version 0.14.0
Visualization of spatial patterns for Milvus milvus observations (Flickr, iNaturalist).
Preparations#
import os, sys
from pathlib import Path
import psycopg2
import geopandas as gp
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import hdbscan
import calendar
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
import matplotlib.patheffects as pe
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
from typing import List, Tuple, Dict, Optional, Any
from IPython.display import clear_output, display, HTML
from datetime import datetime
from pyproj import Transformer
from shapely.geometry import box
module_path = str(Path.cwd().parents[0] / "py")
if module_path not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(module_path)
from modules.base import tools, hll
from modules.base.hll import union_hll, cardinality_hll
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
The autoreload extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext autoreload
OUTPUT = Path.cwd().parents[0] / "out" # output directory for figures (etc.)
WORK_DIR = Path.cwd().parents[0] / "tmp" # Working directory
(OUTPUT / "figures").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
(OUTPUT / "svg").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
WORK_DIR.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
Plot styling
plt.style.use('default')
CRS_WGS = "epsg:4326" # WGS1984
CRS_PROJ = "esri:54009" # Mollweide
# CRS_PROJ = "esri:102014" # Lambert Conformal Conic
Define Transformer ahead of time with xy-order of coordinates
PROJ_TRANSFORMER = Transformer.from_crs(
CRS_WGS, CRS_PROJ, always_xy=True)
Set global font
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'
plt.rcParams['font.serif'] = ['Times New Roman'] + plt.rcParams['font.serif']
Load Milvus range#
This is the habitat range calculated by iNaturalist observations. The area is currently very broad and includes many locations, where Milvus milvus will be only very seldom observable.
DATA_FOLDER = Path.cwd().parents[0] / "00_data" / "milvus"
range_kml = DATA_FOLDER / "range.kml"
from fiona.drvsupport import supported_drivers
supported_drivers['KML'] = 'rw'
df = gp.read_file(range_kml, driver='KML', ignore_geometry=False)
print(df.crs)
epsg:4326
save to Geopackage, for archive purposes
df.to_file(
OUTPUT/ 'Milvusmilvus_range.gpkg', driver='GPKG', layer='Milvus milvus')
project to Mollweide
gdf_range = df.to_crs(CRS_PROJ)
ax = gdf_range.plot()
ax.set_axis_off()

Load Milvus milvus observations#
Load observation data. This data was requested with the iNaturalist Export tool, based on a species search for Milvus. Milvus includes 2 species.
df = pd.read_csv(DATA_FOLDER / "observations-350501.csv")
df.head()
| id | observed_on_string | observed_on | time_observed_at | time_zone | user_id | user_login | user_name | created_at | updated_at | ... | geoprivacy | taxon_geoprivacy | coordinates_obscured | positioning_method | positioning_device | species_guess | scientific_name | common_name | iconic_taxon_name | taxon_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7793 | May 22, 2010 13:59 | 2010-05-22 | 2010-05-22 12:59:00 UTC | London | 446 | kevinandseri | NaN | 2010-07-10 09:15:17 UTC | 2016-06-22 18:30:14 UTC | ... | NaN | open | False | NaN | NaN | Red Kite | Milvus milvus | Rotmilan | Aves | 5267 |
| 1 | 9495 | 2011-01-01 11:29 | 2011-01-01 | 2011-01-01 11:29:00 UTC | London | 351 | zabdiel | John Proctor | 2011-01-01 11:31:50 UTC | 2016-06-22 18:32:46 UTC | ... | NaN | open | False | NaN | NaN | Red Kite | Milvus milvus | Rotmilan | Aves | 5267 |
| 2 | 9496 | 2011-01-01 11:42 | 2011-01-01 | 2011-01-01 11:42:00 UTC | London | 351 | zabdiel | John Proctor | 2011-01-01 11:43:09 UTC | 2016-06-22 18:32:46 UTC | ... | NaN | open | False | NaN | NaN | red kite | Milvus milvus | Rotmilan | Aves | 5267 |
| 3 | 14694 | 2011-04-17 | 2011-04-17 | NaN | London | 654 | spookypeanut | NaN | 2011-04-17 18:18:12 UTC | 2016-06-22 18:44:11 UTC | ... | NaN | open | False | NaN | NaN | Red Kite | Milvus milvus | Rotmilan | Aves | 5267 |
| 4 | 50134 | 2011-10-05 | 2011-10-05 | NaN | Berlin | 4130 | michael | Michael | 2012-02-01 19:59:12 UTC | 2016-06-22 19:39:03 UTC | ... | NaN | open | False | NaN | NaN | Milvus milvus | Milvus milvus | Rotmilan | Aves | 5267 |
5 rows × 39 columns
df.columns
Index(['id', 'observed_on_string', 'observed_on', 'time_observed_at',
'time_zone', 'user_id', 'user_login', 'user_name', 'created_at',
'updated_at', 'quality_grade', 'license', 'url', 'image_url',
'sound_url', 'tag_list', 'description', 'num_identification_agreements',
'num_identification_disagreements', 'captive_cultivated',
'oauth_application_id', 'place_guess', 'latitude', 'longitude',
'positional_accuracy', 'private_place_guess', 'private_latitude',
'private_longitude', 'public_positional_accuracy', 'geoprivacy',
'taxon_geoprivacy', 'coordinates_obscured', 'positioning_method',
'positioning_device', 'species_guess', 'scientific_name', 'common_name',
'iconic_taxon_name', 'taxon_id'],
dtype='object')
milvus_inat = gp.GeoDataFrame(
df, geometry=gp.points_from_xy(df.longitude, df.latitude), crs=CRS_WGS)
milvus_inat.to_crs(CRS_PROJ, inplace=True)
Load world countries geometry
world = tools.get_shapes("world", shape_dir=OUTPUT / "shapes")
Already exists
world.to_crs(CRS_PROJ, inplace=True)
bbox_europe = -25, 35, 35, 59
# convert to Mollweide
minx, miny = PROJ_TRANSFORMER.transform(
bbox_europe[0], bbox_europe[1])
maxx, maxy = PROJ_TRANSFORMER.transform(
bbox_europe[2], bbox_europe[3])
RANGE_COLOR = "#810f7c"
OBSERVATION_COLOR = "red"
Create legend manually
range_patch = mpatches.Patch(
color=RANGE_COLOR,
label='Range, Milvus milvus', alpha=0.4)
obs_patch = mpatches.Patch(
color=OBSERVATION_COLOR,
label='Observations', alpha=0.9)
legend_entries = [range_patch, obs_patch]
legend_kwds = {
"bbox_to_anchor": (1.0, 1),
"loc":'upper left',
"fontsize":8, "frameon":False,
"title":"Milvus milvus", "title_fontsize":8,
"alignment":"left"}
def plot_map(
gdf: gp.GeoDataFrame, x_lim: [Tuple[float, float]] = None, y_lim: [Tuple[float, float]] = None,
gdf_range: gp.GeoDataFrame = None, world: gp.GeoDataFrame = None,
legend_entries: List[mpatches.Patch] = None, legend_kwds: Dict[str, Any] = None,
range_color: str = RANGE_COLOR, observation_color: str = OBSERVATION_COLOR, fig_size: Tuple[int, int] = None,
return_ax: bool = None):
"""Plot a point map with legend and optional range-shape"""
if fig_size is None:
fig_size = (6, 9)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=fig_size)
if gdf_range is not None:
gdf_range.plot(
ax=ax,
facecolor=range_color,
edgecolor=None,
alpha=0.4)
gdf.plot(
ax=ax,
markersize=.1,
facecolor=observation_color,
edgecolor=None,
alpha=0.9)
if world is not None:
world.plot(
ax=ax, color='none', edgecolor='black', linewidth=0.3)
if not None in [x_lim, y_lim]:
ax.set_xlim(*x_lim)
ax.set_ylim(*y_lim)
ax.axis('off')
if not None in [legend_entries, legend_kwds]:
ax.legend(
handles=legend_entries, **legend_kwds)
fig.tight_layout()
if return_ax:
return fig, ax
fig.show()
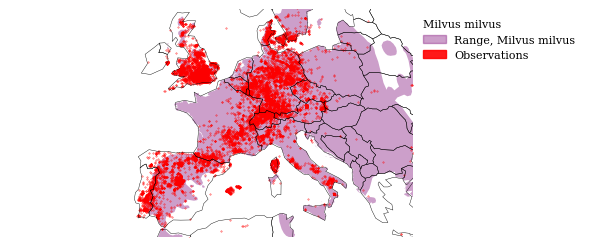
fig, ax = plot_map(
milvus_inat, x_lim=(minx, maxx), y_lim=(miny, maxy),
gdf_range=gdf_range, world=world, legend_entries=legend_entries,
legend_kwds=legend_kwds, return_ax=True)
fig.show()
tools.save_fig(fig, output=OUTPUT, name="milvus_inat_europe")
Zoom in
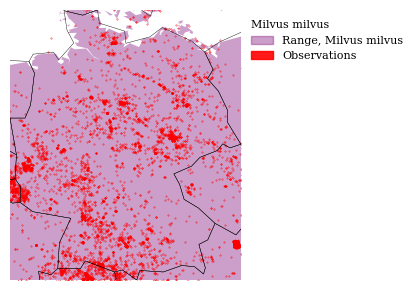
bbox_germany = world[world.index == "Germany"].bounds.values.squeeze()
minx, miny = bbox_germany[0], bbox_germany[1]
maxx, maxy = bbox_germany[2], bbox_germany[3]
plot_map(
milvus_inat, x_lim=(minx, maxx), y_lim=(miny, maxy),
gdf_range=gdf_range, world=world,
legend_entries=legend_entries, legend_kwds=legend_kwds, fig_size=(6,3))
Find clusters (HDBSCAN)#
We just want to see distribution and major clusters. A more interactive approach is shown by João Paulo Figueira’s Geographic Clustering with HDBSCAN
data = np.array(list(zip(df.longitude, df.latitude)))
X = np.radians(data) # convert the list of lat/lon coordinates to radians
earth_radius_km = 6371
epsilon = 0.005 / earth_radius_km # calculate 5 meter epsilon threshold
clusterer = hdbscan.HDBSCAN(min_cluster_size=100, metric='haversine').fit(X)
color_palette = sns.color_palette('deep', len(clusterer.labels_))
cluster_colors = [color_palette[x] if x >= 0
else (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
for x in clusterer.labels_]
cluster_member_colors = [sns.desaturate(x, p) for x, p in
zip(cluster_colors, clusterer.probabilities_)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*data.T, s=10, linewidth=0, c=cluster_member_colors, alpha=0.25)
ax.set_xlim(bbox_europe[0], bbox_europe[1])
ax.set_ylim(bbox_europe[2], bbox_europe[3])
ax.axis('off')
fig.show()

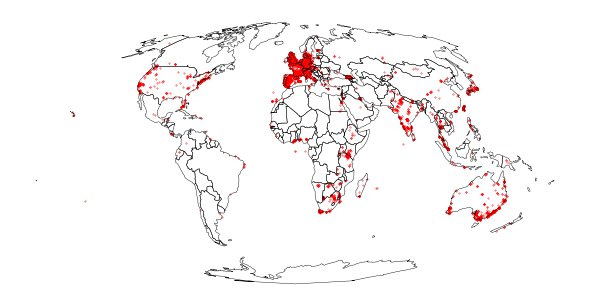
Load Milvus milvus Flickr observations (worldwide)#
flickr_observations = DATA_FOLDER / "2022-02-17_milvusmilvus.csv"
df = pd.read_csv(flickr_observations)
Time format: see Python strftime cheatsheet
load_kwargs = {
"index_col":'datetime',
"parse_dates":{'datetime':["post_create_date"]},
"date_format":'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
"keep_date_col":'False',
"usecols":["post_guid", "post_create_date", "latitude", "longitude"]
}
df = pd.read_csv(flickr_observations, **load_kwargs)
df.head(1)
| post_guid | latitude | longitude | post_create_date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime | ||||
| 2012-10-01 | XSQGXtc9wWIHX6XiEtdaOqgKPURZ7tZtIRere0IA7wQ | 52.246984 | -3.628835 | 2012-10-01 |
milvus_flickr = gp.GeoDataFrame(
df, geometry=gp.points_from_xy(df.longitude, df.latitude), crs=CRS_WGS)
milvus_flickr.to_crs(CRS_PROJ, inplace=True)
plot
plot_map(
milvus_flickr, world=world)
plot_map(
milvus_flickr, world=world, x_lim=(minx, maxx), y_lim=(miny, maxy), fig_size=(4,2))
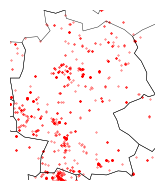
Saxony-Anhalt#
According to Nicolai, Mammen & Kolbe (2017), the highest population of the Red Kite is found in Saxony-Anhalt.
Nicolai, B., Mammen, U., & Kolbe, M. (2017). Long-term changes in population and habitat selection of Red Kite Milvus milvus in the region with the highest population density. VOGELWELT 137: 194–197 (2017)
Below, we visualize this area, merging Flickr and iNaturalist observations.
shapes = tools.get_shapes("de", shape_dir=OUTPUT / "shapes", project_wgs84=False)
Loaded 5.10 MB of 5.11 (100%)..
Extracting zip..
Retrieved vg2500_12-31.utm32s.shape.zip, extracted size: 0.73 MB
We want to filter by Saxony-Anhalt with a buffer of 100 km
geom_saxonya = shapes[shapes.index == "Sachsen-Anhalt"]
Get bounds of Saxony-Anhalt
geom_saxonya_bbox = box(*geom_saxonya.total_bounds)
Project and concat Flickr and iNaturalist observations
milvus_gdf = pd.concat(
[milvus_flickr.to_crs(shapes.crs), milvus_inat.to_crs(shapes.crs)])
Clip observations to bounds of Saxony-Anhalt (only iNat, as there are only 4 Flickr obervations of Milvus in the focus region)
Note: We could also use gp.overlay() here, e.g.:
gdf_select = gp.overlay(
milvus_gdf, geom_saxonya_bbox,
how='intersection')
gdf_select = gp.clip(milvus_inat.to_crs(shapes.crs), mask=geom_saxonya_bbox)
len(gdf_select)
856
Set bounds of Saxony-Anhalt as plotting limits
bbox_saxonya = geom_saxonya.bounds.values.squeeze()
bbox_saxonya
array([ 607181.85913772, 5647848.4600198 , 789161.6620191 ,
5880180.07203066])
minx, miny = bbox_saxonya[0], bbox_saxonya[1]
maxx, maxy = bbox_saxonya[2], bbox_saxonya[3]
bbox_layer = gp.GeoDataFrame(index=[0], crs=shapes.crs.to_epsg(), geometry=[geom_saxonya_bbox])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 3))
ax = milvus_gdf.plot(
ax=ax,
markersize=.1,
facecolor="grey",
edgecolor=None,
alpha=0.9)
ax = bbox_layer.plot(
ax=ax, color='white', edgecolor='black',
linewidth=0.9, linestyle='dashed')
ax = gdf_select.plot(
ax=ax,
markersize=.1,
facecolor=OBSERVATION_COLOR,
edgecolor=None,
alpha=0.9)
ax = shapes.plot(
ax=ax, color='none', edgecolor='black', linewidth=0.3)
ax = shapes[shapes.index == "Sachsen-Anhalt"].plot(
ax=ax, color='none', edgecolor='black', linewidth=1)
buf = 50000 # 50km
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_xlim((minx-buf, maxx+buf))
ax.set_ylim((miny-buf, maxy+buf))
fig.show()
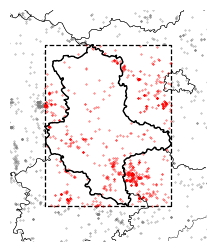
tools.save_fig(fig, output=OUTPUT, name="focus_region")
WGS bounds:
bbox_layer.to_crs(CRS_WGS).bounds.values.squeeze()
array([10.52659544, 50.90971941, 13.30916778, 53.0603523 ])
Update our Europe plot with the bounds of the close-up region.
bbox_europe = -25, 35, 35, 59
# convert to Mollweide
minx, miny = PROJ_TRANSFORMER.transform(
bbox_europe[0], bbox_europe[1])
maxx, maxy = PROJ_TRANSFORMER.transform(
bbox_europe[2], bbox_europe[3])
Update legend
outside_patch = mpatches.Patch(
# color="tab:blue", # default matplotlib blue
color="grey",
label='Outside analysis bounds', alpha=0.9)
if len(legend_entries) > 2:
legend_entries.pop()
legend_entries.append(outside_patch)
bbox_layer.loc[0, "name"] = "Focus Region"
label_off = {
"Focus Region":(-2000000, 500000),
}
label_rad = {
"Focus Region":-0.2,
}
Annotatipn arrow ending at lower-right corner
lower_right = (
bbox_layer.to_crs(CRS_PROJ).bounds.values.squeeze()[2],
bbox_layer.to_crs(CRS_PROJ).bounds.values.squeeze()[1])
fig, ax = plot_map(
milvus_inat, x_lim=(minx, maxx), y_lim=(miny, maxy),
gdf_range=gdf_range, world=world,
legend_entries=legend_entries, legend_kwds=legend_kwds, return_ax=True)
ax = bbox_layer.to_crs(CRS_PROJ).plot(
ax=ax, color='none', edgecolor='white',
linewidth=1.5, linestyle=(0, (1,1)))
tools.annotate_locations(
gdf=bbox_layer, ax=ax, label_off=label_off, label_rad=label_rad,
text_col="name", arrowstyle='->', arrow_col='black', fontsize="small",
coords=lower_right)
fig.show()
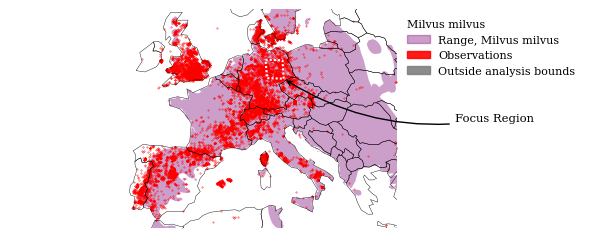
tools.save_fig(fig, output=OUTPUT, name="milvus_inat_europe_annotated")
Create notebook HTML#
References#
Alexander Dunkel and Dirk Burghardt. Assessing Perceived Landscape Change from Opportunistic Spatiotemporal Occurrence Data. Land, 13(7):1091, July 2024. URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/13/7/1091 (visited on 2024-07-22), doi:10.3390/land13071091.
