Spatial Overlays#
Summary
Just like in GIS software, Python allows you to perform spatial overlay operations, which combine multiple spatial datasets based on their locations. In this section explores different types of spatial operations using the overlay() function in GeoPandas.
Load required libraries:
import geopandas as gp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
Define file paths:
INPUT_Path = Path.cwd().parents[0] / "out"
Load input data:
input_data = gp.read_file (INPUT_Path / "clipped.shp")
ax=input_data.plot()
ax.set_axis_off()
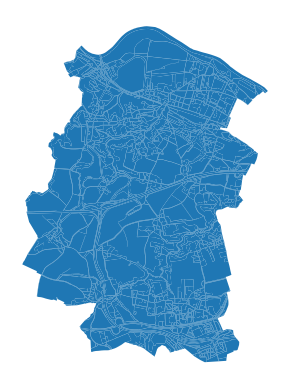
Check the coordinate system:
input_data.crs
Show code cell output
<Projected CRS: EPSG:25833>
Name: ETRS89 / UTM zone 33N
Axis Info [cartesian]:
- E[east]: Easting (metre)
- N[north]: Northing (metre)
Area of Use:
- name: Europe between 12°E and 18°E: Austria; Croatia; Denmark - offshore and offshore; Germany - onshore and offshore; Italy - onshore and offshore; Norway including Svalbard - onshore and offshore.
- bounds: (12.0, 34.79, 18.01, 84.01)
Coordinate Operation:
- name: UTM zone 33N
- method: Transverse Mercator
Datum: European Terrestrial Reference System 1989 ensemble
- Ellipsoid: GRS 1980
- Prime Meridian: Greenwich
Load overlay data:
Show code cell source
# District data from the Dresden portal Already mentioned in the Clipping Data chapter
import requests
geojson_url = "https://kommisdd.dresden.de/net4/public/ogcapi/collections/L137/items"
response = requests.get(geojson_url)
if response.status_code == 200:
gdf = gp.read_file(geojson_url)
else:
print("Error:", response.text)
overlay_data= gdf[gdf['id']== '99']
ax=overlay_data.plot()
ax.set_axis_off()
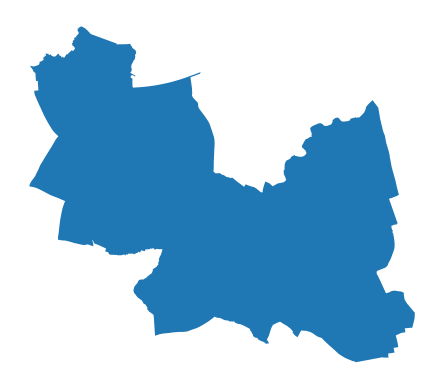
Check the coordinate system:
overlay_data.crs
Show code cell output
<Geographic 2D CRS: EPSG:4326>
Name: WGS 84
Axis Info [ellipsoidal]:
- Lat[north]: Geodetic latitude (degree)
- Lon[east]: Geodetic longitude (degree)
Area of Use:
- name: World.
- bounds: (-180.0, -90.0, 180.0, 90.0)
Datum: World Geodetic System 1984 ensemble
- Ellipsoid: WGS 84
- Prime Meridian: Greenwich
In case the coordinate system of the layers are different match the coordinates using to_crs method.
overlay_data = overlay_data.to_crs(input_data.crs)
The overlay() function in GeoPandas allows different types of spatial operations, defined by the how parameter.
The following list explains available operations:
intersection– Returns the overlapping (shared) area between two geometries.union- Merges both geometries into a single geometry.difference- Subtract second geometry from the first geometry.symmetric_difference- The areas that are in either of the two geometries, but not in bothidentity- Keeps the shape of the first geometry while adding overlapping parts from the second geometry.
Overlay Analysis
For more information, check the GeoPandas spatial overlay documentation.
Examples how to apply these operations:
# Intersection: Find the overlapping (shared) area between input_data and overlay_data
out_intersection = gp.overlay(
input_data, overlay_data,
how='intersection')
# Union: Merge input_data and overlay_data into one geometry
out_union = gp.overlay(
input_data, overlay_data,
how='union')
# Difference: Subtract overlay_data from input_data
out_difference = gp.overlay(
input_data, overlay_data,
how='difference')
# Symmetric Difference: Get areas that are in either geometry, but not both
out_symmetric = gp.overlay(
input_data, overlay_data,
how='symmetric_difference')
# Identity: Retain the first geometry but mark overlapping areas with the second geometry
out_identity = gp.overlay(
input_data, overlay_data,
how='identity')
/tmp/ipykernel_2565/1074488158.py:7: UserWarning: `keep_geom_type=True` in overlay resulted in 42 dropped geometries of different geometry types than df1 has. Set `keep_geom_type=False` to retain all geometries
out_union = gp.overlay(
/tmp/ipykernel_2565/1074488158.py:17: UserWarning: `keep_geom_type=True` in overlay resulted in 42 dropped geometries of different geometry types than df1 has. Set `keep_geom_type=False` to retain all geometries
out_symmetric = gp.overlay(
The results can be inspected by using the print function, which will show the first few rows of the overlayed dataset.
Example:
print(out_symmetric.head())
CLC_st1 Biotpkt201 Shape_Leng Shape_Area id bez bez_lang \
0 112 7.150000 122.271774 457.162617 NaN NaN NaN
1 311 16.503069 315.595049 3746.157997 NaN NaN NaN
2 211 6.336151 2119.697191 138157.775431 NaN NaN NaN
3 211 6.336151 1130.132105 60835.673105 NaN NaN NaN
4 324 14.000424 435.445295 4721.684346 NaN NaN NaN
flaeche_km2 sst sst_klar historie aend \
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
4 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
geometry
0 POLYGON ((404140.322 5654373.512, 404139.007 5...
1 POLYGON ((403977.642 5654356.446, 403988.445 5...
2 POLYGON ((405646.102 5654518.48, 405646.102 56...
3 MULTIPOLYGON (((402546.984 5654396.33, 402546....
4 POLYGON ((402599.505 5654413.851, 402593.69 56...
The results can be visualized by using the plot function.
Example:
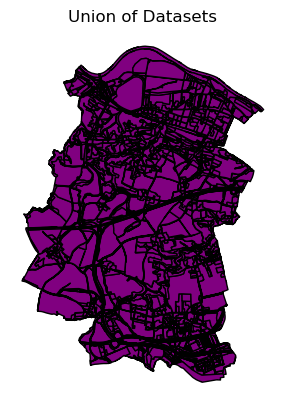
ax = out_union.plot(
color="purple",
edgecolor="black")
ax.set_title("Union of Datasets")
ax.set_axis_off()
ax = out_intersection.plot(
color="green",
edgecolor="black")
ax.set_title("Intersection of Datasets")
ax.set_axis_off()
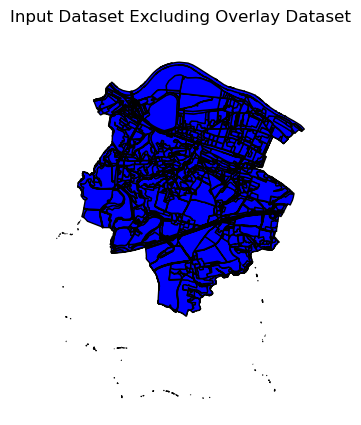
ax = out_difference.plot(
color="blue",
edgecolor="black")
ax.set_title("Input Dataset Excluding Overlay Dataset")
ax.set_axis_off()